This article describes the seven types of curriculum and classroom implications. Upon reading this article, you will realize the complexity of the term “curriculum” as I discuss each type, along with the examples. Read on and find out the different types.
Allan Grathon (2000), as cited by Bilbao et al. (2008), describes the seven types of the curriculum in the following section.
Table of Contents
Seven Types of Curriculum
The following are the 7 types of curriculum that are being implemented in schools worldwide.
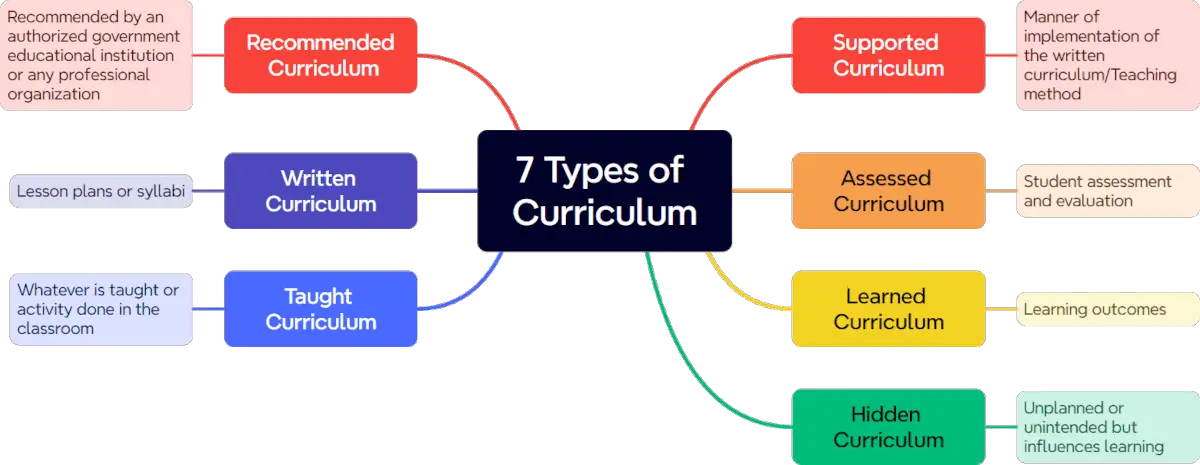
1. Recommended Curriculum
Perhaps you have asked these questions: Why should I take all these subjects and follow the course flow religiously? Why is there a need to implement the K to 12? The answer is simple! The Ministry of Education, the Commission on Higher Education, or any professional organization can recommend and implement a curriculum.
For example, in the Philippines, the curriculum being implemented by the Department of Education (DepEd) or the Commission on Higher Education (CHEd) is an example of a recommended curriculum. In some cases, a law-making body like the congress and the senate, or a university or a school can recommend a subject, a course, or any academic program deemed necessary for national identity and security, for environmental protection and sustainable development, among others.
2. Written Curriculum
The written curriculum refers to a lesson plan or syllabus written by teachers. Another example is the one written by curriculum experts with the help of subject teachers. This kind of written curriculum needs to be pilot tested or tried out in sample schools to determine its effectiveness.
Related Post: Development and Examples of a Written Curriculum
3. Taught Curriculum
The taught curriculum refers to the instructional practices and learning activities that are actually implemented in the classroom by teachers. This is where the written curriculum comes to life through the various teaching methods and strategies employed by educators.
When teachers deliver lectures, facilitate group discussions, guide students through hands-on experiments, or assign project-based learning activities, they are demonstrating the taught curriculum. The goal of the taught curriculum is to address the diverse needs and interests of students by utilizing a range of teaching and learning styles.
For example, a teacher may choose to use direct instruction for introducing new content, collaborative learning for promoting critical thinking, or inquiry-based activities for developing scientific skills. Through the taught curriculum, teachers create dynamic learning experiences that allow students to actively engage with the material and work towards mastering the knowledge and competencies outlined in the written curriculum. Ultimately, the taught curriculum serves as the bridge between the prescribed learning objectives and the actual learning that takes place in the classroom.

4. Supported Curriculum
The supported curriculum is about the implementation of the written curriculum. Whatever is being taught or activity being done in the classroom is a taught curriculum.
Let’s break this down further for clarity and compare the supported curriculum to the taught curriculum discussed in the previous section.
The Supported Curriculum
The supported curriculum refers to the resources, materials, and infrastructure that enable the implementation of the written curriculum. This includes things like textbooks, technology, lab equipment, learning aids, and any other physical or digital resources that teachers use to deliver instruction. The supported curriculum ensures that teachers have the necessary tools and materials to effectively teach the content and skills outlined in the written curriculum.
The Taught Curriculum
The taught curriculum is the actual instruction and learning activities that take place in the classroom, as facilitated by the teacher. This is where the written curriculum is brought to life through the teaching methods, strategies, and learning experiences employed by the teacher. When teachers give lectures, facilitate group work, lead lab experiments, and use various teaching styles, they are demonstrating the taught curriculum.
The taught curriculum is designed to address the diverse needs and interests of students by incorporating different teaching and learning approaches.
Key Differences
To sum it up, the supported curriculum lays the foundation, while the taught curriculum is the dynamic, student-centered application of the curriculum in the classroom setting. They are complementary components of the overall curricular process.
5. Assessed Curriculum
When students take a quiz or the mid-term and final exams, these evaluations are the so-called assessed curriculum. Teachers may use the pencil and paper tests and authentic assessments like portfolio assessment and performance-based assessments to know if the students are progressing or not.
6. Learned Curriculum
This type of curriculum indicates what the students have learned. The capability that students should demonstrate at the end of the lesson can be measured through learning outcomes.
A learning outcome can be manifested by what students can perform or do either in their cognitive, affective, or psychomotor domains. The test results can determine the learning outcome, and the students can achieve it through learning objectives.
Related Post: Learning Outcomes 101: A Comprehensive Guide
7. Hidden Curriculum
The hidden curriculum refers to the unplanned or unintended curriculum but plays a vital role in learning. It consists of norms, values, and procedures. See the two-minute video below for more details.
Classroom Implications of the Different Types of Curriculum
Now, let’s discuss some classroom implications of the different curriculum types by taking the following situation as an example.
Let’s assume that you are a college student taking up Bachelor of Secondary Education, major in English. Your course or degree program is a recommended curriculum prescribed by CHED. The syllabi given to you by your teachers are the written curriculum. When your teachers start to teach, that is a taught curriculum. And when they ask you to use the internet and search for information about future-oriented topics like regenerative medicine as a very effective but noninvasive approach to better health, this is a supported curriculum.
Furthermore, teachers need to evaluate your performance. So, when you are given a test or exam, that is the assessed curriculum. The assessed curriculum results will determine what you have learned—and that is the so-called learned curriculum. However, the hidden curriculum can affect what will be taught and assessed by your teachers and eventually affect what you will learn.
To sum it up, the curriculum is not only about a course or a simple listing of subjects, but it is the total learning experience of students as indicated by the seven types of curriculum.
Related Post: Example of a Curriculum on Environmental Science
Recent Advances in Curriculum Development
As advances in curriculum development occur, there emerged a transformative approach to teaching and learning that has been gaining momentum in recent years—the creative curriculum. This approach paved the way for the design of a curriculum that integrates traditional academic disciplines with real-world applications, tapping into students’ inherent curiosity to foster an engaging and collaborative learning environment.
Since ChatGPT came into being in November 2022, software-based curriculum applications that use artificial intelligence emerged as the best way forward in designing an appropriate curriculum for learners of varied needs. Innovative, responsive, and up-to-date curriculum powered by the so-called curriculum engine can be designed quickly and more reliably with efficient use of digital resources.
This article presents 10 of the major theories of education including a description of the theory with diagrams and contributions to the development of education as we know today.
Suggested Related Readings
- An Introduction to Curriculum Engine
- Creative Curriculum: Concepts and Examples
- Blended Website Learning Model: Excellent Solution to Forced Online Education Due to the COVID-19 Pandemic
Reference
Bilbao, P. P., Lucido, P. I., Iringan, T. C., and R. B. Javier (2008). Curriculum development. Quezon City: Lorimar Publishing, Inc.
© M. G. Alvior | Updated 16 August 2025



What are the examples of overt curriculum
can you give example on classroom curriculum here is the question.
1.realism
2.idealism
3.perennialism
4.existentialism
5.pragmatism. .
Hi.reflection based on the question :what do you think will happen to our curriculum if we have no trifocalized system of education?
Hi.reflection based on the qurstion :what do you think will happen to our curriculum if we have no trifocalized system of education?
Pls help me reason out why does hidden curriculum needed in the school
Please I need more clarification on null curriculum
Hi can you give example on classroom curriculum here is the question. ..cite specific classroom curriculum situation that reveal the fallowing. .
1.realism
2.idealism
3.perennialism
4.existentialism
5.pragmatism. ..Thanks
From the types of curriculum identified, is there really the so called “best curriculum”? How these types of curriculum prepare students to become productive and purposeful individual in the society?
Hello Ma’am, Kindly explain the content of this link just briefly? The terms are different and it has more content. or maybe, what you mentioned are the types of curriculum used in the Philippines, while in the link that I’m going to paste here are in other countries? I don’t know. thanks you very much for taking the time answering. https://thesecondprinciple.com/instructional-design/types-of-curriculum/
Hi, Annabelle. If you take a look at the contents and the explanations, they are almost similar. The terms are synonymous though the author had categorized the types in different ways and added some more. Thank you.
What an inspiring message from you, Matthew! Thank you so much.
wow what a site ..am impressed….but i still cant give enough information on how Electronic curriculum positively influence teaching and learning
Thank you, Helalia. Your topic must be a separate one. If I have time, I will write about it or conduct a research in that field. That is the emerging topic nowadays.
Hi, why curriculum is important to study as a student teacher, what are the points?
Hello, Chuube. My article about the Meaning and Importance of Curriculum Development can help you answer it. Curriculum is the heart of any learning institution that’s why it is very important. In the article above, try to summarize everything and you will get the points. Remember, you can’t study or take a subject without it. The same as true as the teacher.
How written curriculum,taught or implemented curriculum and received curriculum are related
Hi, Beatha. They are related because when you teach (taught curriculum), that is the process when you are implementing the curriculum. The implemented curriculum can be referred to the actual teaching and learning process.
hi. this is amazing I really found it helpful long live.
You are most welcome, Marcelle.
thank you ma’am!
it’s very helpful and educative…
what do you think is an effective curriculum?
in what ways can educational objectives be attained?
I want to fnd out what is the developmental curriculum and where i can fiind information on it.
should I get the details about the following
1.what is curriculum research
2.types of curriculum research
3.process of curriculum research
4.important of curriculum research
Hi, Arone. If you read the article above, I mentioned Grathon. There is a typo error. The name is Allan Glatthorn. Please click the link, http://www1.udel.edu/educ/whitson/897s05/files/Glatthorn10.pdf
Thanks a lot.
sorry madam!!!!. I have a question . What are the different scholars who tried to classify the types of curriculum?